Source: The Hindu (GDP slows down)
Context:
The National Statistics Office (NSO) released its first advance estimates of GDP for FY 2024-25, projecting a growth rate of 6.4%, the slowest in four years. This projection is critical for policymakers, particularly as the Union Budget for 2025-26 is being prepared.
UPSC Relevance:
Prelims:
- Important Terms:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Gross Value Added (GVA)
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
- Sectoral Trends: Agriculture, Manufacturing, Public Administration.
Mains (GS Paper III):
- Economic Development:
- Challenges in maintaining high GDP growth.
- Role of government expenditure and fiscal policies.
- Issues with Private Investment:
- Reasons for sluggish investment despite favourable conditions.
- Policy Implications:
- Need for targeted fiscal stimulus to revive growth engines.
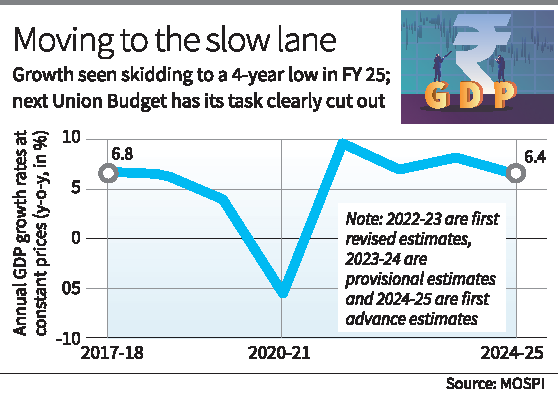
Key Highlights of NSO’s GDP Projections:
GDP and GVA Growth:
- Real GDP Growth:
- Estimated at 6.4% in 2024-25, down from 8.2% in 2023-24.
- Economy rebounded in the second half of the fiscal year with an estimated growth of 6.8% after clocking 6% in the first half.
- Gross Value Added (GVA):
- Projected to grow at 6.4%, compared to 7.2% in 2023-24.
- Sectoral Growth:
- Agriculture: Growth expected at 3.8% (up from 1.4% last year).
- Public Administration, Defence & Other Services: Projected at 9.1% (from 7.8% last year).
- Manufacturing: Slows to 5.3%, a significant drop from 9.9% in 2023-24.
- Mining and Quarrying: Growth at 2.9%, down from 7.1%.
Concerns Over Investment Growth:
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF):
- Indicator of fresh investments, projected to grow at just 6.4%, compared to 9% in 2023-24.
- Decline attributed to reduced government capital expenditure and sluggish private sector investment, despite favorable conditions.
- Construction Sector:
- Growth pegged at 8.6%, lower than 9.9% last year.
Expenditure-Side Analysis:
- Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE):
- Expected to rise 7.3%, indicating improved household spending compared to 4% last year.
- Government Final Consumption Expenditure (GFCE):
- Projected to grow 4.1%, up from 2.5% in 2023-24.
Economic Implications of GDP slow down for Budget 2025-26:
- Key Challenge: Restoring GDP growth to 7%-plus levels achieved in preceding years.
- Impact of Monetary Policies:
- The RBI’s interest rate hikes and tighter lending norms have contributed to the slowdown.
- Lower fiscal stimulus has also played a role in tempering growth.
Expert Opinions:
- Dharmakirti Joshi (Crisil Chief Economist):
- Slower growth in 2024-25 attributed to high interest rates, reduced government spending, and sluggish private investment.
- A sharper focus on boosting private investments is critical.
- Madhavi Arora (Emkay Global Financial Services):
- The advance estimates are based on limited data available till November and are prone to revisions.


